Economic impact of the French-Canadian cultural community in 2021
Impact on GDP is close to $6 billion
This report offers national and provincial estimates of the economic impact of Francophone arts, culture, and heritage outside of Quebec in 2021. It is my translation of a French-language report that I prepared for the Fédération culturelle canadienne-française in November of 2023.
Included are estimates of the direct, indirect and induced impacts of cultural activity. Direct impacts are defined as the value added to gross domestic product (GDP) of spending in the cultural sector. Indirect impacts measure the new spending that is generated by the expenses of cultural organizations (e.g., by suppliers). Induced impacts capture the spending that is generated by the earnings of cultural workers and suppliers.
The analysis is based on three Statistics Canada products: culture indicators by province and territory, the 2021 census, and input-output multipliers. In general, the analysis is detailed and defensible, but it is also pragmatic. It is based on the proportion of Francophones in cultural occupations, rather than surveys of the cultural sector, which would be a very large undertaking.
The calculation of the proportion of Francophones in cultural occupations is based on a new linguistic definition produced by Statistics Canada for the 2021 census: "potential demand for federal communications and services in the minority official language". This relatively broad definition includes people outside of Quebec whose mother tongue is French and/or who speak French at home, either as the language spoken most often or secondarily. In total, there are 1.4 million people outside of Quebec who could potentially request federal services in French.
Detailed notes regarding the methods and products that are used in the calculations can be found at the end of this report.
National results
The economic impact of the French-Canadian cultural community (outside of Quebec) is estimated at $5.63 billion in 2021.
This estimate includes:
A direct impact of $2.76 billion.
An indirect impact of $1.67 billion.
An induced impact of $1.20 billion.
According to a custom request from the 2021 census, there are 36,100 cultural workers outside of Quebec who speak French, or 5.2% of all cultural workers outside of Quebec. This proportion is used in the GDP estimates in this report.
The total value of Francophone cultural production outside of Quebec (essentially total revenues) amounts to $5.32 billion. This is the starting point for estimates of the indirect and induced impacts.
Provincial results
Newfoundland and Labrador
The impact of the arts, culture, and heritage of Newfoundland and Labrador's Francophone community on the province's GDP is $14.9 million in 2021. There is an additional GDP impact of $3.5 million in other provinces, for a total impact of $18.4 million across Canada.
The impact in NL includes:
A direct impact of $10.1 million.
An indirect impact of $3.3 million.
An induced impact of $1.5 million.
Francophone cultural production in the province (essentially total revenues) amounts to $17.7 million.
150 Francophone cultural workers reside in NL, representing 2.2% of the province’s cultural workers, according to Hill Strategies’ analysis of the 2021 census.
Prince Edward Island
The impact of Francophone arts, culture, and heritage on the GDP of Prince Edward Island amounts to $18.3 million in 2021. In addition, there is an impact of $5.5 million in other provinces, resulting in a total impact of $23.9 million across the country.
The PEI estimate includes:
A direct impact of $13.6 million.
An indirect impact of $3.0 million.
An induced impact of $1.7million.
The total value of Francophone cultural production on the Island (essentially total revenues) is estimated at $21.9 million in 2021.
There are 190 Francophone cultural workers in PEI, or 7.3% of all cultural workers in the province.
Nova Scotia
The impact of the arts, culture, and heritage of Nova Scotia’s Francophone community on the province's GDP is $141 million in 2021. The impact on the GDP of other provinces is estimated at $33 million, for a total impact of $174 million across Canada.
The GDP estimate in NS includes:
A direct impact of $92 million.
An indirect impact of $30 million.
An induced impact of $18 million.
The total value of Francophone cultural production in Nova Scotia in 2021 (essentially total revenues) amounts to $162 million.
The province is home to 1,100 Francophone cultural workers, or 5.6% of all cultural workers in NS.
New Brunswick
The impact of Francophone arts, culture, and heritage on New Brunswick’s GDP is estimated at $576 million in 2021. The impact on the GDP of other provinces amounts to $157 million, resulting in an overall impact of $733 million across the country.
The estimate of the impact in New Brunswick includes:
A direct impact of $389 million.
An indirect impact of $121 million.
An induced impact of $66 million.
Francophone cultural production in NB (essentially total revenues) totals $646 million in 2021.
In New Brunswick, there are 3,900 Francophone cultural workers, representing 34% of the province’s cultural workers, according to Hill Strategies’ analysis of the 2021 census.
Ontario
Francophone arts, culture, and heritage has an impact of $3.07 billion on Ontario’s GDP in 2021. There is an additional GDP impact of $0.27 billion on other provinces, bringing the total impact across Canada to $3.34 billion.
The provincial estimate includes:
A direct impact of $1.61 billion.
An indirect impact of $0.86 billion.
An induced impact of $0.60 billion.
In Ontario, Francophone cultural production (essentially total revenues) is estimated at $3.2 billion.
According to Hill Strategies’ analysis of data from the 2021 census, Ontario is home to 20,800 Francophone cultural workers, or 5.6% of the province’s cultural workers.
Manitoba
The impact of Francophone arts, culture, and heritage on Manitoba’s GDP is $159 million in 2021. The impact on other provinces’ GDP equals $43 million, for a total impact of $202 million across the country.
The GDP estimate in MB includes:
A direct impact of $103 million.
An indirect impact of $30 million.
An induced impact of $25 million.
The total value of Francophone cultural production in Manitoba (essentially total revenues) is $194 million in 2021.
There are 1,400 Francophone cultural workers in Manitoba, or 5.8% of the province’s cultural workers.
Saskatchewan
In 2021, the impact of the arts, culture, and heritage of Saskatchewan’s Francophone community on the province's GDP is $77 million. A further GDP impact of $17 million accrues to other provinces, bringing the total impact across the country to $93 million.
The estimate of the impact in Saskatchewan includes:
A direct impact of $50 million.
An indirect impact of $15 million.
An induced impact of $11 million.
Francophone cultural production in SK (essentially total revenues) is estimated at $88 million in 2021.
The province’s 520 Francophone cultural workers represent 3.2% of all cultural workers in Saskatchewan.
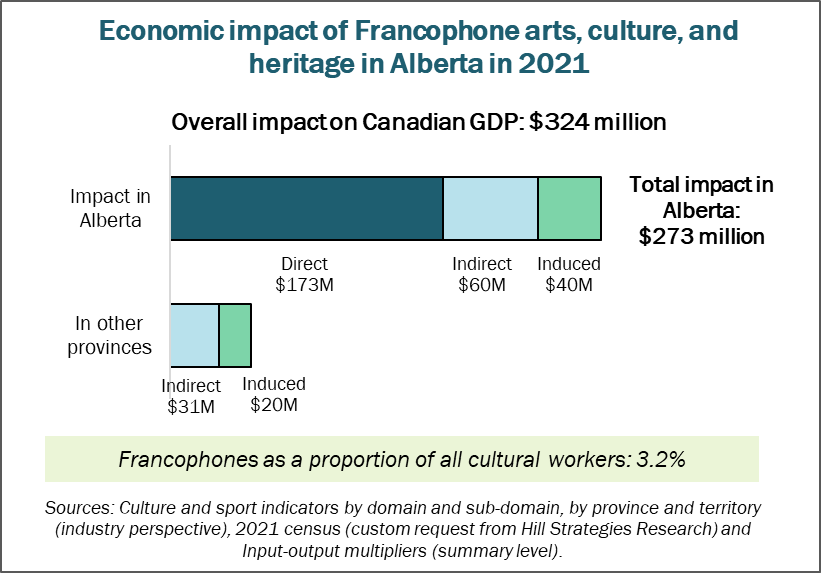
Alberta
Francophone arts, culture, and heritage has an impact of $273 million on Alberta’s GDP in 2021. The impact on other provinces’ GDP is $51 million, for a total impact of $324 million across the country.
The Alberta estimate includes:
A direct impact of $173 million.
An indirect impact of $60 million.
An induced impact of $40 million.
The total value of Francophone cultural production in AB (essentially total revenues) is $307 million in 2021.
In Alberta, there are 2,600 Francophone cultural workers, accounting for 3.2% of the province’s cultural workers.
British Columbia
The impact of the arts, culture, and heritage of British Columbia’s Francophone community on the province's GDP is $709 million in 2021. There is an additional GDP impact of $142 million in other provinces, resulting in an overall impact of $851 million across the country.
The GDP estimate in BC includes:
A direct impact of $393 million.
An indirect impact of $167 million.
An induced impact
of $148 million.
Francophone cultural production in the province (essentially total revenues) is estimated at $761 million in 2021.
The province is home to 5,300 Francophone cultural workers, or 3.4% of BC’s cultural workers, based on Hill Strategies’ analysis of the 2021 census.
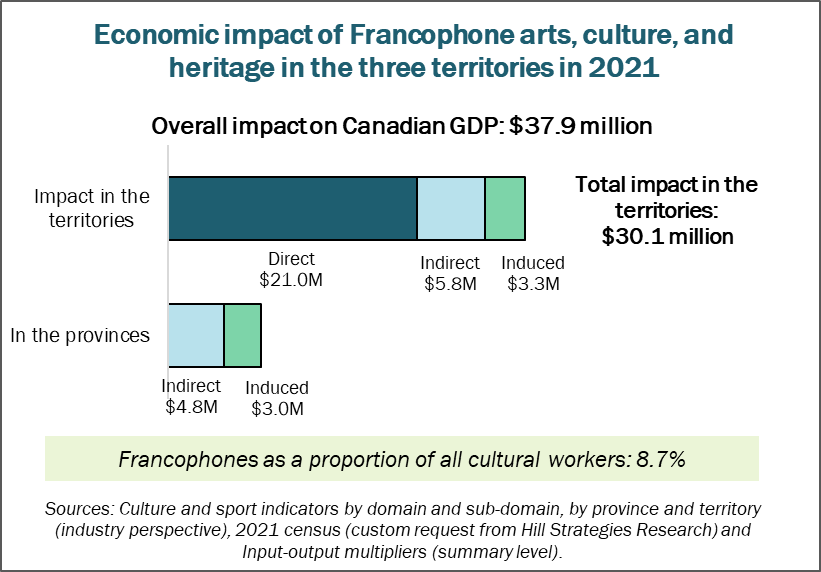
Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut
Francophone arts, culture, and heritage has an impact of $30.1 million on the GDP of the three territories in 2021. The impact on the provinces’ GDP equals $7.8 million, for a total impact of $37.9 million across Canada.
The estimate of the impact in the territories includes:
A direct impact of $21.0 million.
An indirect impact of $5.8 million.
An induced impact of $3.3 million.
The total value of Francophone cultural production in the three territories (essentially total revenues) is estimated at $38 million in 2021.
There are 230 Francophone cultural workers in the territories, or 8.7% of all cultural workers.
Notes on methods
Statistics Canada defines culture as "creative artistic activity and the goods and services produced by it, and the preservation of heritage". The economic impact calculations in this report generally follow this definition, which was established in the Conceptual Framework for Culture Statistics, 2011. However, translators were the only writing occupation omitted from the Conceptual Framework for Culture Statistics. We have chosen to include translators among the 52 occupation groups that we use to measure workers in the arts, culture, and heritage.
The following points summarize other important choices made in developing the economic impact estimates in this report.
For all calculations:
Calculations for Canada outside of Quebec are based on calculations for individual provinces and territories.1
Statistics on the direct impact of culture (in total, i.e., all languages combined) are drawn from Statistics Canada's Culture and sport indicators by domain and sub-domain, by province and territory (industry perspective). Statistics Canada does not break down these indicators by language.
The Francophone share of the economic impact of culture outside of Quebec comes from the proportion of Francophones in 52 cultural occupations. According to our analysis of 2021 census data, there are 36,100 Francophones who work in cultural occupations outside of Quebec, representing 5.2% of the 688,500 cultural workers outside of Quebec. The census data come from a special data request by Hill Strategies Research.
The 52 cultural occupation groups include occupations in performing arts, sound recording, film, video, broadcasting, libraries, archives, galleries, museums, other heritage institutions, architecture, design, publishing, and printing.
The definition of "Francophone" in this report is based on the potential demand for federal communications and services in the minority official language. This definition includes people with French as their mother tongue and/or those who speak French at home, whether it is the language spoken most often or secondarily.
This report uses the most recent economic statistics and multipliers. It is not ideal that the economic statistics to relate to 2021, while the multipliers are from 2019. Nevertheless, in our opinion, the best way to proceed in this situation is to use the most recent data available.
For the estimates of direct impact:
The most recent estimate of the direct impact of culture is from 2021. For that year, the overall direct impact (all languages combined) of the cultural sector on GDP outside of Quebec is $53 billion.
Given that the proportion of Francophones in the 52 cultural occupations is 5.2%, the direct impact of Francophone culture outside of Quebec is estimated at 5.2% of $53 billion, or $2.76 billion.
For the estimates of indirect, induced, and overall impacts:
The indirect and induced impacts were calculated using Statistics Canada's national and provincial input-output multipliers for 2019 (the most recent year). These multipliers are commonly used in this type of analysis.2 In general, they are two years behind the estimates of the direct impact of culture in the provinces and territories.
Statistics Canada’s multipliers cover fairly broad sub-sectors. We have chosen the two most "cultural" sub-sectors: Information and cultural industries (which includes publishing, film, sound recording, and broadcasting) and Arts, entertainment, and recreation (which includes the performing arts and heritage). Unfortunately, these two sub-sectors extend beyond the cultural sector to include telecommunications, data processing and hosting, spectator sports, lotteries, and entertainment. This is an imperfect choice, but the best possible choice, in our opinion.
To produce a single multiplier for Canada and for each province, we calculated the average of the multipliers for these two sub-sectors. This average was applied to the total revenues from cultural activities (called "production" by Statistics Canada) to calculate the indirect and induced impacts.
Because Statistics Canada offers estimates of the direct economic impact of culture expressed in terms of basic prices, we have chosen the multipliers for indirect and induced impacts that are expressed in terms of basic prices, rather than market prices.
The value of cultural production (all languages combined) outside of Quebec is $102 billion in 2021.
The value of Francophone cultural production outside of Quebec in 2021 is estimated at $5.32 billion, or 5.2% of $102 billion.
Most – but not all – economic impact analyses include indirect and induced impacts. In our opinion, these impacts are valid, but not everyone agrees on this matter. For example, The Culture, Arts, Heritage and Sport Economic Impact Model, developed by Statistics Canada and Canadian Heritage, includes indirect and induced impacts. However, Statistics Canada's Culture indicators only provide estimates of the direct impact.
The estimates in this report do not take into account ancillary spending by cultural attendees on items such as accommodation, food, and transportation. These amounts are difficult to measure, not universally agreed upon, and often excluded from economic impact studies.
For these calculations, we have retained the input-output multipliers for Canada as a whole, rather than an average of the multipliers for the provinces and territories outside of Quebec.
For example, The Culture, Arts, Heritage and Sport Economic Impact Model, developed by Statistics Canada and Canadian Heritage, is based on these multipliers.